Linked List 链表
Linked List 链表
单项链表实现
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
T206. 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
**进阶:**链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
Solution:迭代
使用三个pre,cur,next指针,分别记录上一个节点,本节点,下一个节点。
迭代每一个节点:先用next指向cur的下一个节点,然后把cur的下一个节点指向pre,最后再把pre指向cur,cur指向next。
当cur到null时,表明已经是末尾了,返回pre即为最后(也是翻转后的第一个)节点
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur!=null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
Solution:递归
递归也有两种解法:
一种是返回翻转后链表的新的头部,然后把自身的后继节点的指针指向自己,自己指向空来完成翻转,再继续返回头部。
一种是返回翻转后链表的新的尾部,不停返回新链表的尾部,再把自身插入尾部构成新的尾部,这样需要一个额外的递归参数来保存新的头部。
第一种:返回新链表的头部
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = recurison(head);
return newHead;
}
private ListNode recurison(ListNode cur){
if (cur.next == null){
return cur;
}
//获取到新的头部
ListNode newHead = recurison(cur.next);
//把自身后继节点的指针指向自己,完成翻转
ListNode nextNode = cur.next;
nextNode.next = cur;
//再把自身的指针删掉
cur.next = null;
return newHead;
}
}
第二种:返回新链表的尾部
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode newTail = recurison(head, newHead);
newTail.next = null;//新链表尾部要指向空,否则会形成环
return newHead.next;
}
private ListNode recurison(ListNode node, ListNode newHead){
if (node.next == null){
newHead.next = node;
return node;
}
ListNode nextNode = recurison(node.next, newHead);
//把新的尾部指向自己,这样自己就是新的尾部
nextNode.next = node;
return node;
}
}
T25. K 个一组翻转链表
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
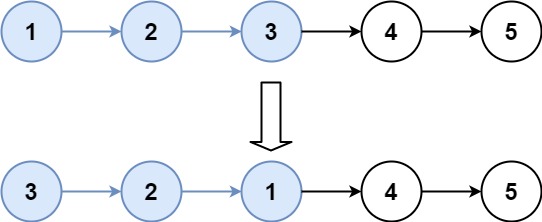
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
提示:
- 链表中的节点数目为
n 1 <= k <= n <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 1000
**进阶:**你可以设计一个只用 O(1) 额外内存空间的算法解决此问题吗?
Solution
我们可以对每k个小的片段复用上面题目所设计的翻转链表,然后连起来即可
因此需要保留的数据有
- 上一个片段的最后一个元素
lastSegEnd,用于连接本片段翻转后的第一个元素 - 下一个片段的第一个元素
nextSegStart,用于本片段最后一个元素连接下一个片段
由于第一个片段不存在 lastSegEnd因此设计一个 dummyLastSegEnd指向这个片段
循环结束的条件是,不存在下一个片段了,或者下一个片段没有k个node
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummyLastSegEnd = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode lastSegEnd = dummyLastSegEnd;
ListNode start = lastSegEnd.next;
while (start!=null){
ListNode end = lastSegEnd;
//Move the end pointer to the end of the segment
for (int i=0; i < k; i++){
if (end.next == null){
//When reach the end of the linked list, return
return dummyLastSegEnd.next;
}
end = end.next;
}
//Record the head of the next segment
ListNode nextSegStart = end.next;
//Reverse the segment
end.next = null;
ListNode newStart = reverseList(start);
ListNode newEnd = start;
//Connect the two segment
lastSegEnd.next = newStart; // This seg to pre seg
newEnd.next = nextSegStart; // This seg to next seg
//Move to the nextSegment
lastSegEnd = newEnd;
start = nextSegStart;
}
return dummyLastSegEnd.next;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur!=null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
T23. 合并 K 个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length0 <= k <= 10^40 <= lists[i].length <= 500-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4lists[i]按 升序 排列lists[i].length的总和不超过10^4
Solution
采用 优先队列 来解题:每次将最小元素出队,然后把该元素链接的下一元素入队。
class Solution {
static Comparator<ListNode> cmp = new Comparator<>() {
public int compare(ListNode n1, ListNode n2) {
return n1.val - n2.val;
}
};
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
Queue<ListNode> prique = new PriorityQueue<>(cmp);
int k = lists.length;
//检查为空的情况
if (k==0){
return null;
}
//把每一个链表的非空头节点入队, 并检查是否有可能是空链表
for (int i=0; i<k; i++){
if (lists[i] != null){
prique.offer(lists[i]);
}
}
if (prique.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
//记录首个节点
ListNode head = prique.poll();
if (head.next != null){
prique.offer(head.next);
}
//出队最大节点,再将该节点的下一个非空节点入队,重复直到队列为空
ListNode temp = head;
while (!prique.isEmpty()){
ListNode cur = prique.poll();
temp.next = cur;
if (cur.next != null){
prique.offer(cur.next);
}
temp = cur;
}
return head;
}
}